Your smart contract just hit a wall. It needs real-time compliance data, cross-chain datafeeds, data from the web, or to execute arbitrary code—but it’s trapped in the blockchain’s walled garden.
What if your contract could just execute arbitrary JavaScript, call any API, and return cryptographically verified results—all without pre-deploying oracle infrastructure?
Introducing Truebit’s Dynamic Oracles: simply include code and API calls in your transaction, trigger offchain execution, and receive verified results back on-chain—all with zero upfront infrastructure.
In this guide, you’ll build and experience a complete Dynamic Oracle—from custom JavaScript logic to verified on-chain callbacks.
The Oracle Problem: Opacity, Friction, and Limited Auditability
Blockchain smart contracts face a fundamental limitation: they cannot natively execute computational tasks beyond the EVM’s deterministic operations or fetch external data.
Existing oracle solutions address data retrieval but create new problems:
Opacity of Computation: Traditional oracles only attest to final results, not the process itself, leaving users to trust black-box operations without visibility into how data was processed.
Deployment Friction: Existing systems require pre-registration and deployment of both computational logic and oracle infrastructure before any smart contract can use them, creating significant overhead.
Limited Auditability: When oracles lack a verifiable data processing record, one cannot retroactively verify whether results were computed correctly, making dispute resolution impossible.
Siloed interactions: Static oracles lack data flows to or from other blockchains. They cannot query cross-chain state or return verified results to multiple destination chains simultaneously.
These restrictions are particularly problematic for regulated applications like Real World Asset (RWA) tokenization and compliance verification, where auditability and provenance are mandatory.
Truebit Dynamic Oracles (in beta) eliminate these tradeoffs by providing an on-demand oracle system with full execution transparency and cryptographic verification.
Dynamic Oracles: Zero-Friction Verifiable Data & Computation for Smart Contracts
Dynamic Oracles are smart contract interactions that enable blockchain transactions to trigger arbitrary offchain computation and data retrieval with cryptographic verification.
Flexible data processing: Your contract executes JavaScript or TypeScript code, API calls, and cross-chain queries—all specified at transaction time, not deployment time.
Auditable execution: Each step generates cryptographic proof of correctness with code swiftly executed by offchain nodes participating in interactive verification games.
Cross-chain return results: Dynamic oracles callback results to smart contracts on any blockchain where Truebit’s WatchTower contracts exist.
For developers, this paradigm shift translates directly into massive productivity gains and a significantly improved user experience.
Quick Start: Your First Dynamic Oracle Contract
Let’s build a simple contract that demonstrates the core pattern; we’ll request offchain computation and handle verified results.
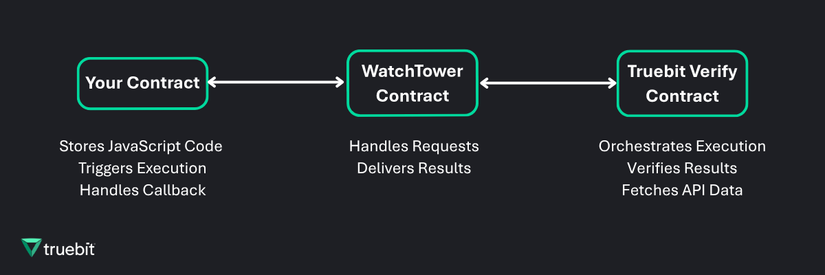
Step 1: Understand the architecture
Dynamic Oracles uses a “WatchTower” contract to bridge requests and responses to and from Truebit Verify.
Step 2: Write Javascript Logic
Let’s write a simple Fibonacci function for demonstration purposes. This is the code we want to execute offchain:
function main(n) {
// Handle base case
if (n <= 1) return n;
// Iterative computation to avoid stack overflow
let a = 0, b = 1;
for (let i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
let temp = a + b;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
return b;
}
// Print the result for an embedded JS function execution to be retrieved in the callback
console.log(main(parseInt(Input)));
Input logged and sent to the main function in the code above represents the value sent from the smart contract to the offchain JavaScript execution environment.
Step 3: Create your User Contract (The “FibonacciCalculator” Contract)
Your smart contract can integrate both Solidity and JavaScript. The JS code is sent to Truebit Verify as a string, and results come back through a callback function.
FibonacciCalculator.sol
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
// Enum for Dynamic Oracle execution types
library DOTypes {
enum ExecutionType {
EMBEDDED_FUNCTION
}
}
// WatchTower Interface used to request execution
interface IWatchTower {
function requestExecution(
string calldata methodSignature,
bytes calldata input,
bytes32 codeHash,
DOTypes.ExecutionType executionType
) external returns (uint256);
}
/**
* @title FibonacciCalculator
* @notice Fibonacci numbers off-chain using Truebit's Dynamic Oracles
* @dev Shows the basic pattern: store code, trigger execution, handle callback
*/
contract FibonacciCalculator {
// Immutable WatchTower contract reference
IWatchTower public immutable watchTower;
// State variables to check last execution result
uint256 public lastWTExecutionId;
uint256 public lastResult;
// Custom errors
error NotwatchTower(address sender);
// Events for tracking computation lifecycle
event FibonacciRequested(
uint256 wtExecutionId,
address indexed requester,
uint256 n,
uint256 timestamp
);
event FibonacciComputed(
address indexed requester,
uint256 result,
string[] transcripts,
uint256 wtExecutionId,
uint8 status,
string _callbackMessageDetails,
uint256 timestamp
);
// Ensure we only get callbacks from the WatchTower contract
modifier onlywatchTower() {
if (msg.sender != address(watchTower)) {
revert NotwatchTower(msg.sender);
}
_;
}
/**
* @notice Constructor - initializes with WatchTower
* @param watchTowerAddress Address of the Truebit WatchTower contract
*/
constructor(address watchTowerAddress) {
watchTower = IWatchTower(watchTowerAddress);
}
/**
* @notice Returns the WatchTower contract address
* @return Address of the WatchTower
*/
function getWatchTowerAddress() external view returns (address) {
return address(watchTower);
}
/**
* @notice Returns the last execution result
* @return wtExecutionId The WatchTower execution ID
* @return result The computed Fibonacci result
*/
function getLastExecutionResult() external view returns (uint256 wtExecutionId, uint256 result) {
return (
lastWTExecutionId,
lastResult
);
}
/**
* @notice Returns the JavaScript code for Fibonacci computation
* @dev This is a helper function to keep code organized
* @return JavaScript function as a string
*/
function getTaskSource() public pure returns (string memory) {
return string(abi.encodePacked(
"function main(n) { ",
" if (n <= 1) return n; ",
" let a = 0, b = 1; ",
" for (let i = 2; i <= n; i++) { ",
" let temp = a + b; ",
" a = b; ",
" b = temp; ",
" } ",
" return b; ",
"}",
"console.log(main(parseInt(Input)));"
));
}
/**
* @notice Request Fibonacci computation for a given n
* @dev This function triggers off-chain execution via WatchTower
* @param n The Fibonacci number to compute (F(n))
*/
function requestFibonacci(uint256 n) external {
require(n < 100, "n too large - choose n < 100");
bytes32 codehash = keccak256(bytes(getTaskSource()));
bytes memory payload = abi.encode(n);
uint256 id = watchTower.requestExecution(
string(abi.encodePacked("fibonacci(uint256)")),
payload,
codehash,
DOTypes.ExecutionType.EMBEDDED_FUNCTION
);
lastWTExecutionId = id;
emit FibonacciRequested(id, msg.sender, n, block.timestamp);
}
// At this point:
// 1. WatchTower detects the execution request
// 2. Truebit platform fetches the code to execute within the codehash
// 3. Off-chain nodes execute the JavaScript with input 'n'
// 4. Results are verified through interactive verification games
// 5. WatchTower calls back to callbackTask() with verified result
/**
* @notice Callback function invoked by WatchTower with verified result
* @dev Only callable by WatchTower (enforced by onlywatchTower modifier)
* @param resultData ABI-encoded result from off-chain computation
* @param transcripts Array of transcripts from execution
* @param wtExecutionId The WatchTower execution ID
* @param status Status code (0 == success, 1 == error, 2 == exceeded)
* @param _callbackMessageDetails Additional details about the callback
*/
function callbackTask(
bytes calldata resultData,
string[] memory transcripts,
uint256 wtExecutionId,
uint8 status,
string memory _callbackMessageDetails
) external onlywatchTower {
uint256 result;
if (status == 0) {
result = abi.decode(resultData, (uint256));
} else {
result = 0;
}
lastResult = result;
emit FibonacciComputed(
msg.sender,
result,
transcripts,
wtExecutionId,
status,
_callbackMessageDetails,
block.timestamp
);
}
}
Let’s unpack the code above: when your smart contract calls requestFibonacci(n), it triggers offchain execution via the WatchTower contract.
Step 4: Deployment
Your contract’s callback function will get called with verified results and a reference to the task’s execution ID.
Let’s deploy and test this contract; we are using Hardhat for testing and deployment, but you can use any framework.
Let’s install Hardhat and configure it (in this example we use Hardhat V2), then we can create a deployment script:
npm init -y
npm pkg set type="commonjs"
npm install --save-dev hardhat@^2.19.0 @nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox@^4.0.0
# IMPORTANT: This is a necessary folder to contain the contract(s) to be deployed
mkdir -p contracts
hardhat.config.js
require("@nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox");
module.exports = {
solidity: "0.8.24",
networks: {
"mainnet": {
url: "https://api.avax.network/ext/bc/C/rpc",
chainId: 43114,
accounts: ["<YOUR PRIVATE KEY>"]
}
}
};
deploy.js
const { ethers } = require("hardhat");
const fs = require("node:fs");
const path = require("node:path");
async function main() {
const network = await ethers.provider.getNetwork();
console.log(`Deploying to network: ${network.name} (chainId: ${network.chainId})`);
// Truebit Watchtower Address for DO execution
const WATCHTOWER_ADDRESS = '0xEAd039cA35B9c6592B638C0C4E2b7f42F078B754';
console.log("Deploying FibonacciCalculator contract...");
const [deployer] = await ethers.getSigners();
console.log(`Deploying with account: ${deployer.address}`);
const FibonacciCalculator = await ethers.getContractFactory("FibonacciCalculator");
const fibonacciCalculator = await FibonacciCalculator.deploy(WATCHTOWER_ADDRESS);
await fibonacciCalculator.waitForDeployment();
const contractAddress = await fibonacciCalculator.getAddress();
console.log("FibonacciCalculator deployed to:", contractAddress);
// Save the address to a config file
const config = {
contractAddress: contractAddress,
watchTowerAddress: WATCHTOWER_ADDRESS,
deployerAddress: deployer.address,
deployedAt: new Date().toISOString()
};
fs.writeFileSync(
path.join(__dirname, `${network.name}-contract-config.json`),
JSON.stringify(config, null, 2)
);
console.log(`Contract address information saved in: ${network.name}-contract-config.json`);
return contractAddress;
}
main()
.then(() => process.exit(0))
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exit(1);
});
Step 5: Try it!
requestFibonacci.js
const { ethers } = require("hardhat");
const fs = require('node:fs');
const path = require('node:path');
async function main() {
// Request Fibonacci computation for n=10 for example
const n = 10;
let contractAddress;
try {
const network = await ethers.provider.getNetwork();
console.log(`Executing in network: ${network.name} (chainId: ${network.chainId})`);
// Load contract address from config
const configPath = path.join(__dirname, `${network.name}-contract-config.json`);
const config = JSON.parse(fs.readFileSync(configPath, 'utf8'));
contractAddress = config.contractAddress;
console.log("Using contract address from config:", contractAddress);
// Load contract ABI
const abiPath = path.join(__dirname, './artifacts/contracts/FibonacciCalculator.sol/FibonacciCalculator.json');
const artifactData = JSON.parse(fs.readFileSync(abiPath, 'utf8'));
const [signer] = await ethers.getSigners();
const contract = new ethers.Contract(contractAddress, artifactData.abi, signer);
console.log(`Using signer: ${signer.address}`);
console.log(`Requesting Fibonacci computation for n=${n}...\n`);
const tx = await contract.requestFibonacci(n);
console.log(`Transaction hash: ${tx.hash}`);
const receipt = await tx.wait();
console.log(`\nTransaction confirmed in block ${receipt.blockNumber}`);
console.log(`Gas used: ${receipt.gasUsed.toString()}`);
console.log(`Status: ${receipt.status === 1 ? 'Success' : 'Failed'}`);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error requesting Fibonacci:");
console.error(error.message);
if (error.message.includes("contract-config.json")) {
console.error("\nPlease deploy the contract first:");
console.error("npx hardhat run deploy.js");
}
process.exitCode = 1;
}
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});
getLastExecution.js
const { ethers } = require("hardhat");
const fs = require('node:fs');
const path = require('node:path');
async function main() {
try {
const network = await ethers.provider.getNetwork();
console.log(`Executing in network: ${network.name} (chainId: ${network.chainId})`);
console.log("Fetching Fibonacci last results...\n");
const configPath = path.join(__dirname, `${network.name}-contract-config.json`);
const config = JSON.parse(fs.readFileSync(configPath, 'utf8'));
const contractAddress = config.contractAddress;
console.log(`Using contract address: ${contractAddress}\n`);
const abiPath = path.join(__dirname, './artifacts/contracts/FibonacciCalculator.sol/FibonacciCalculator.json');
const artifactData = JSON.parse(fs.readFileSync(abiPath, 'utf8'));
const provider = ethers.provider;
const contract = new ethers.Contract(contractAddress, artifactData.abi, provider);
console.log("Calling last result saved...\n");
const lastResult = await contract.getLastExecutionResult();
console.log("=== Fibonacci Task Last Execution ===\n");
console.log(`WatchTowerExecutionId: ${lastResult.wtExecutionId}`);
console.log(`Result: ${lastResult.result}\n`);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error fetching last results:");
console.error(error.message);
if (error.message.includes("contract-config.json")) {
console.error("\nPlease deploy the contract first:");
console.error("npx hardhat run deploy.js --network <network-name>\n");
}
process.exitCode = 1;
}
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});
Project preview
Hardhat command execution
# Deploy the testing contract with the specified network
npx hardhat run deploy.js --network mainnet
# Generate a request for fibonacci execution through DO and Truebit platform
npx hardhat run requestFibonacci.js --network mainnet
# Get the last execution after execution through DO and Truebit platform
npx hardhat run getLastExecution.js --network mainnet
Ready to Get Started?
Dynamic Oracles are available in beta on Truebit Verify for Avalanche and Ethereum. Contact us at hello@truebit.io
→ View developer documentation
In Part II we will show you how to use Dynamic Oracles to do cross-chain calls and create an effective bridge for cross-chain compliance verification.

